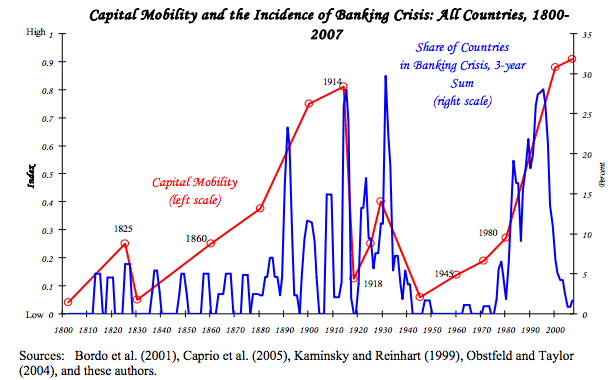
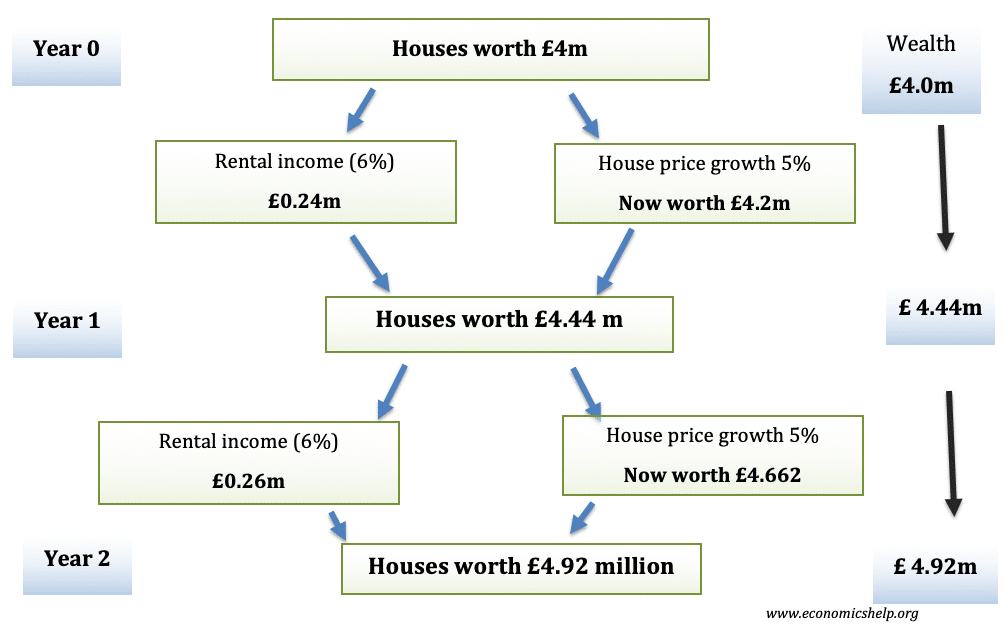
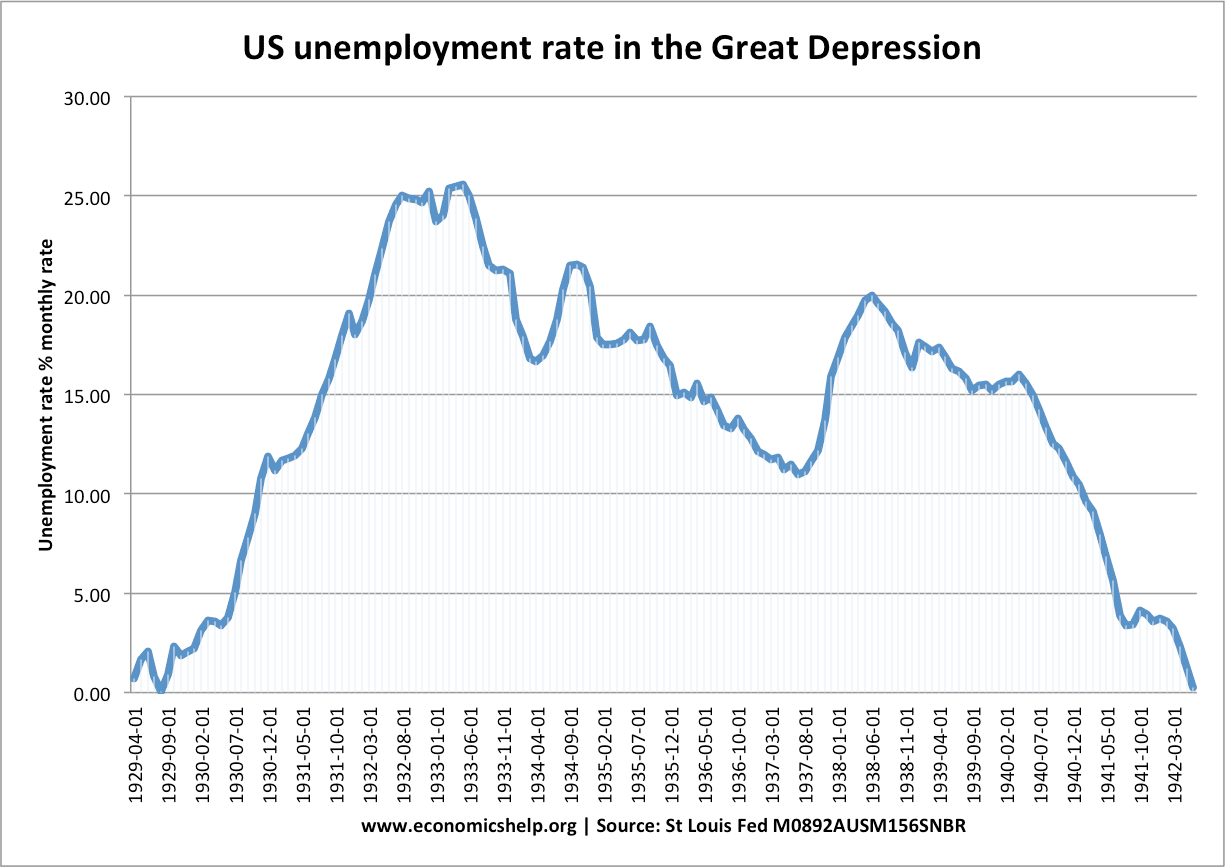
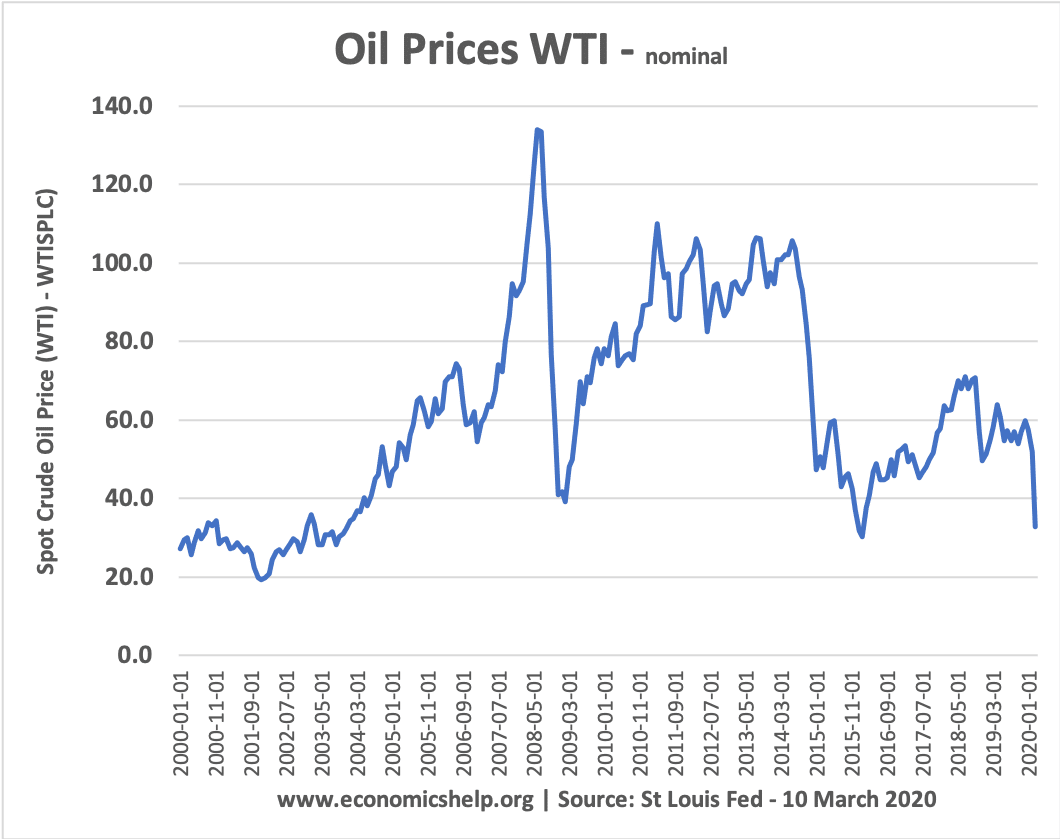
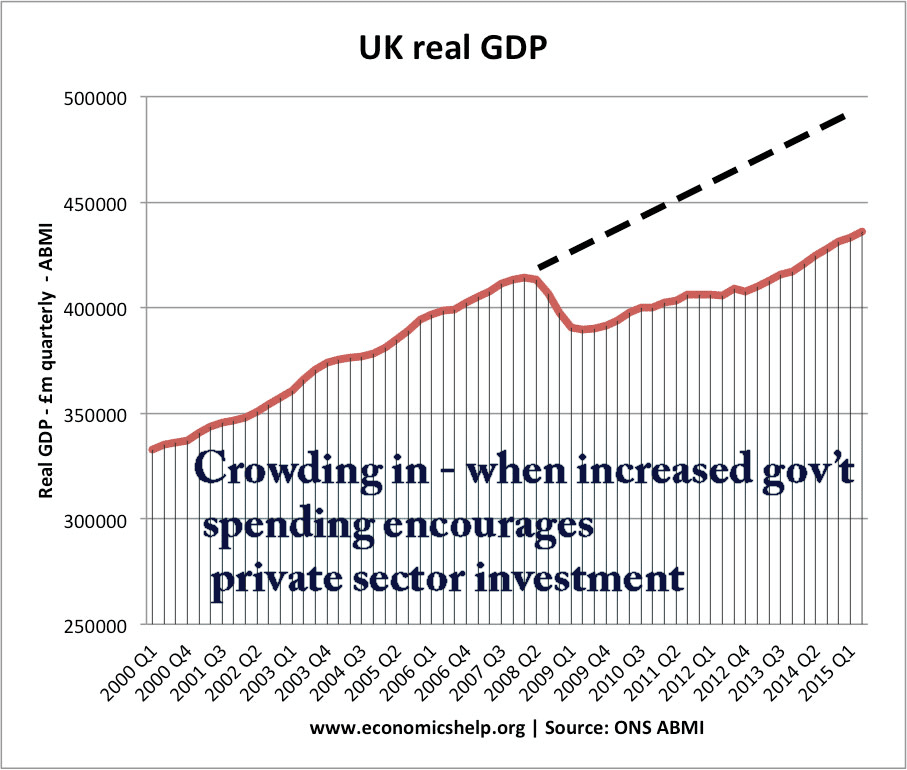
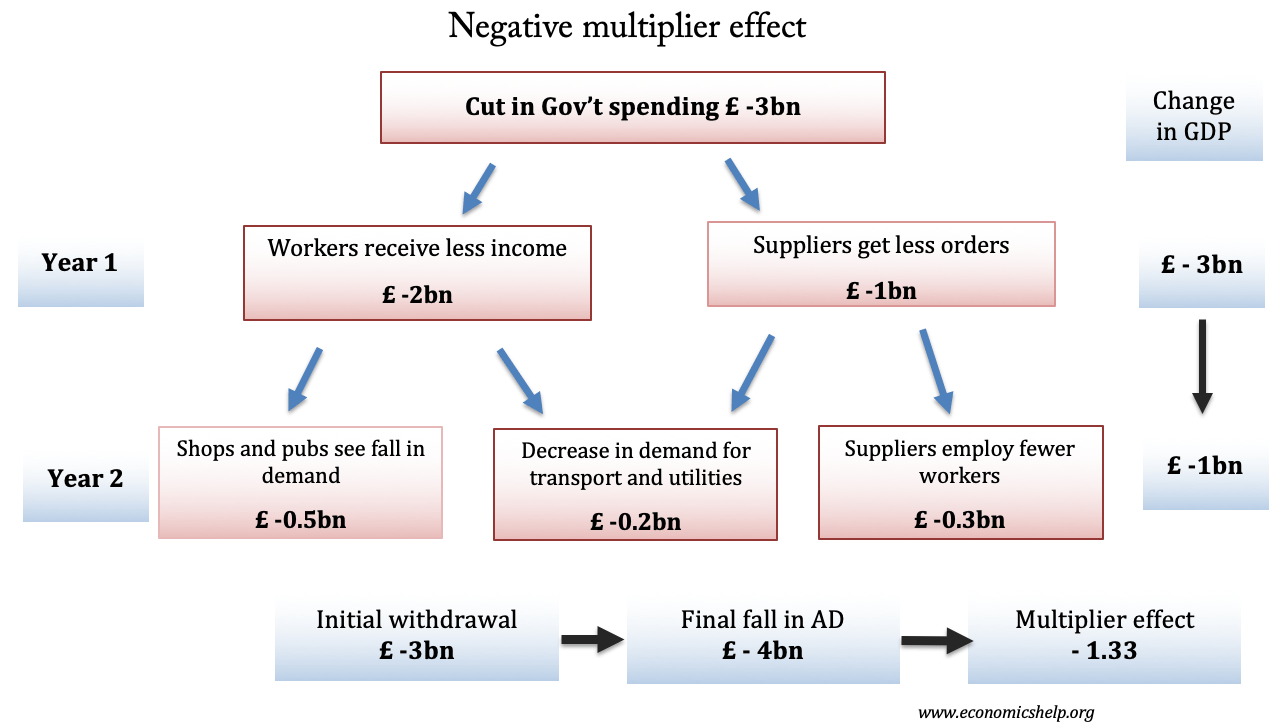
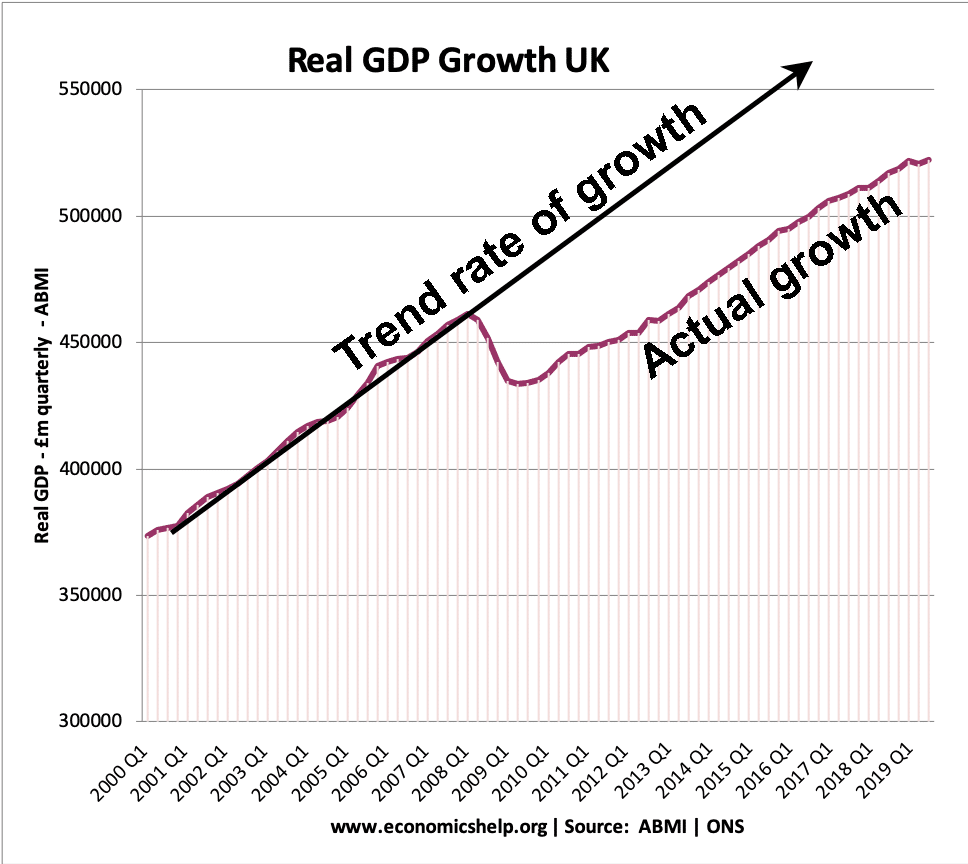
Pros and cons of capital controls
Capital controls are government measures to limit the flow of financial capital and financial assets. Capital controls include limits on foreign currency exchange, limits on the purchase of assets and taxes on financial transfers. Some economists argue that capital controls can help limit destabilising capital flows which cause banking crisis and economic booms and busts. …