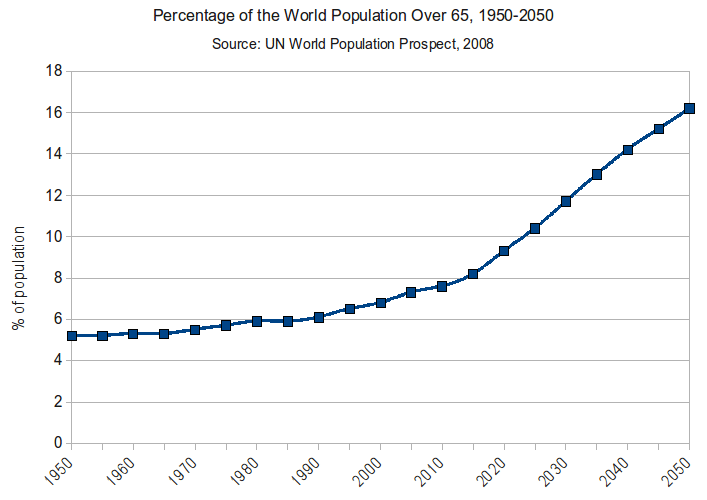
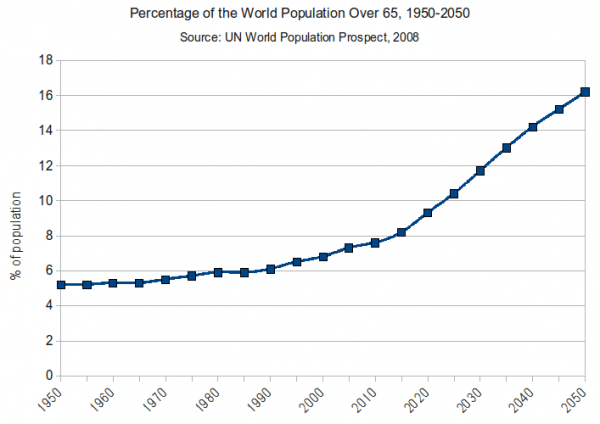
What are the implications of an ageing population? An older population presents many challenges to labour markets, government tax, government spending and the wider economy.
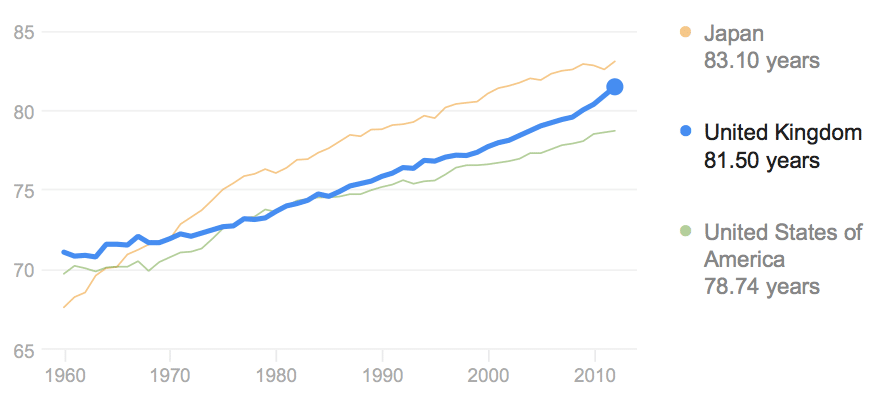
One of the great achievements of the Twentieth Century is a dramatic rise in life expectancy. For example, life expectancy in the US has increased from 45 in 1902 to 75.7 in 2004 (link). Even in the past 50 years, life expectancy has risen in most western economies.
Life expectancy
However, increased life expectancy combined with declining birth rates have caused many to worry about the impact of an ageing population. Frequently, we hear about ‘a demographic time bomb,’ and the fear future generations will struggle to meet an ever increasing number of retired workers and pension commitments.
But, are we correct to be worrying about an ageing population?
Firstly, in the UK, the ratio of people of working age – to people over 65 could fall from 3.7 to 1 in 1999 to 2.1 to 1 in 2040. (BBC) This suggests a very big increase in the dependency ratio and is consequently a cause for concern because, with current spending pension commitments, it will place a higher burden on the shrinking working population.
However, others argue it is a mistake to base calculations solely on a fixed retirement age of 65. If life expectancy increases dramatically, you would expect a sensible policy is to allow some increase in the retirement age, e.g. keeping the same % of your working life for retirement. The UK government has already made tentative steps to raise the retirement age and increase the role of private-sector pensions. These policies will make an ageing population more manageable.
In recent years, the impact of an ageing population in the UK has also been mitigated by a rise in net migration levels. Though, with the UK’s exit from the EU, there is an expectation net migration levels will fall. A side-effect of lower migration will be a faster rise in the dependency ratio.
Main impact of an ageing population
- Increase in the dependency ratio. If the retirement age remains fixed, and the life expectancy increases, there will be relatively more people claiming pension benefits and fewer people working and paying income taxes. The fear is that it will require high tax rates on the current, shrinking workforce.
- Increased government spending on health care and pensions. Also, those in retirement tend to pay lower income taxes because they are not working. This combination of higher spending commitments and lower tax revenue is a source of concern for Western governments – especially those with existing debt issues and unfunded pension schemes.
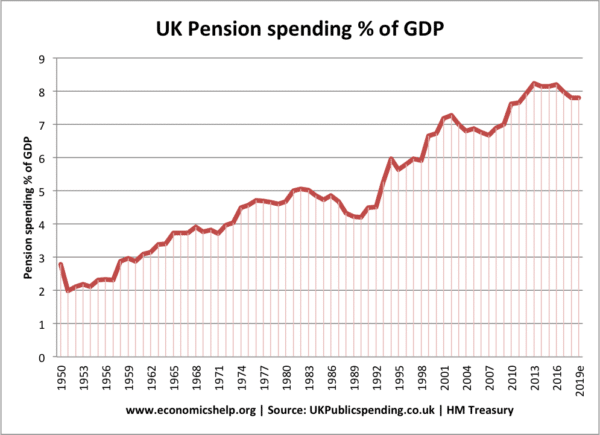
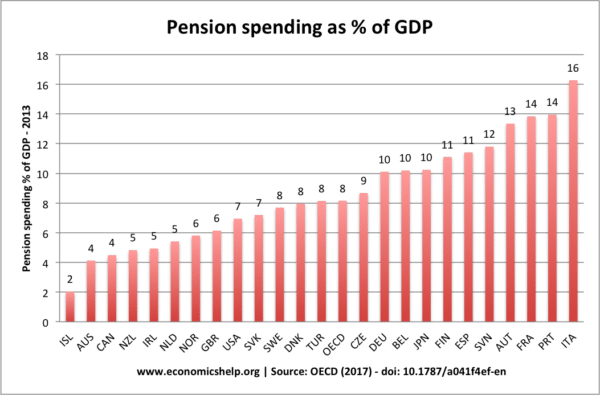
How UK spending on pensions has increased
- Those in work may have to pay higher taxes. This could create disincentives to work and disincentives for firms to invest. Therefore there could be a fall in productivity and growth.
- Shortage of workers. An ageing population could lead to a shortage of workers and hence push up wages causing wage inflation. Alternatively, firms may have to respond by encouraging more people to enter the workforce, by offering flexible working practices.
- Changing sectors within the economy. An increase in the number of retired people will create a bigger market for goods and services linked to older people (e.g. retirement homes)
- Higher savings for pensions may reduce capital investment. If society puts a higher % of income into pension funds, it could reduce the amount of savings available for more productive investment, leading to lower rates of economic growth.
Evaluation of an ageing population
- A declining birth rate also means a smaller number of young people. This will save the government money because young people require education and pay little, if any, taxes. Though the net cost of retired people is greater than the net cost of young people under 18.
- It depends on the health and mobility of an ageing population. If medical science helps people live longer, but with poor mobility, there will be less chance to work. If people live longer and can remain physically active for longer, the adverse impact will be less.
- Immigration could be a potential way to defuse the impact of an ageing population because immigration is primarily from people of working age. However, immigration brings its own political challenges and has become increasingly unpopular, despite net migration creating a positive net fiscal effect.
- Increasing the retirement age is one solution to an ageing population. But, the effect of a higher retirement age will not be felt equally. Those with private savings may be able to still retire early, those with low income paid jobs are more likely to have to keep working. Also, the impact of longer working life will be felt more by manual workers who will find it harder to keep working.
- Population demographics have been shifting for the past few centuries. This is not the first time we have had shifts in the age profile of the population.
- How will it be funded? A big issue is whether spending commitments are funded or unfunded. Many western governments fund their pension plans through pay as you go, rather than saving national insurance contributions. This could lead to gaps in spending commitments.
- Incentives to keep working? Part of the problem is that there is currently a strong incentive for people to retire early. The effective marginal tax rate imposed on earnings resulting from delayed retirement has in many systems been in excess of 60 percent (link) These incentives have encouraged many to take early retirement. Also, there is often a rule prohibiting people working longer – even if they wanted to. If these incentives can be changed, we could increase the number of people working for longer and reduce the dependency burden.
- Economic growth. A big factor in determining the impact of an ageing population is future rates of economic growth. There is a concern, western economies have entered a period of secular stagnation – falling growth rates. This decline in economic growth will increase the pressure on public finances from an ageing population. Strong economic growth, increases tax revenues and makes it easier to fund pension commitments. But, in recent years we have seen stagnant wages and a decline in real incomes of young people. This places stress on redistribution of income from the young to retired. The problem is that an ageing population is one reason put forward for secular stagnation in a country like Japan.
- Inequality. Another problem with an ageing population is that it could exacerbate inequality. With increased reliance on private sector savings, there could be a division between those with a good private sector pension, and those who rely on a diminishing state pension. Also, inequality could be exacerbated by the state of the housing market, with homeowners in a much better position than those who have to continue to rent into their retirement.