Readers Question: Who exactly is the UK is in Debt to? Please can you simplify and explain?
There are two types of debt:
- Government debt (Public sector debt / National debt) – The money the government has borrowed, primarily from the private sector.
- External debt. Liabilities the UK owe to the rest of the world – this is both private sector and public sector.
Who does the government borrow from?
The UK government borrows mainly from
- UK pension funds/insurance companies (29%)
- Private corporations / other financial institutions
- UK building societies. (e.g. building societies buy government gilts to invest their savings to get a decent return.)
- UK Banks
- UK Private investors
- Foreign investors (foreign banks and foreign investment firms (2018 approx 20%)
- Bank of England Asset Purchase facility (Quantitative easing)
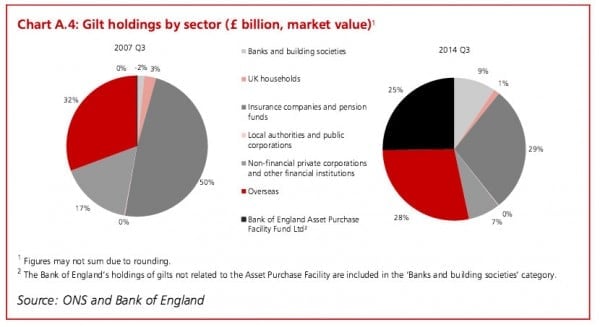
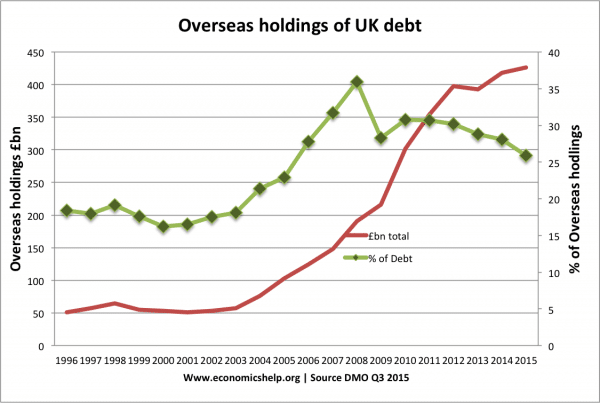
Change in debt composition 2003-2018
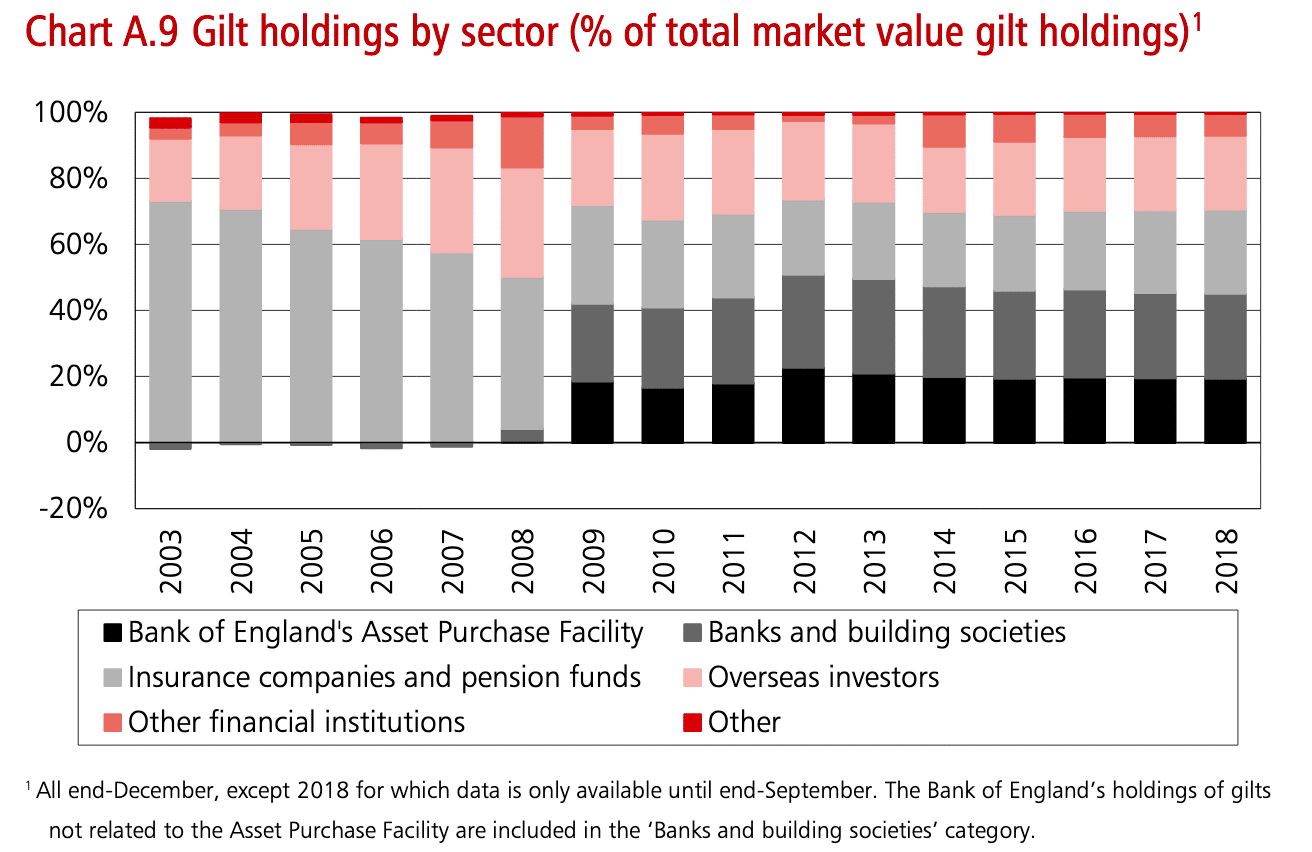
This shows overseas investors hold approx 20% of UK gilts.
Example
- A pension fund will be interested in purchasing UK government gilts to gain a secure return on long-term investment.
- A charity/firm with excess savings may purchase government gilts to get a good interest rate while it decides how to use the money. Retained profit from UK companies has increased in recent years, and corporations have become a bigger buyer of UK gilts.
- A private individual may purchase gilts as part of a balanced portfolio of investment.
We owe money to ourselves
One feature of UK government borrowing is that 75% of the debt we are borrowing from UK citizens and UK institutions. It is like a transfer of pension funds to the government.
Foreign holdings of UK Debt
How much does the government owe to foreign nationals?
UK Debt held by overseas investors (source: DMO)